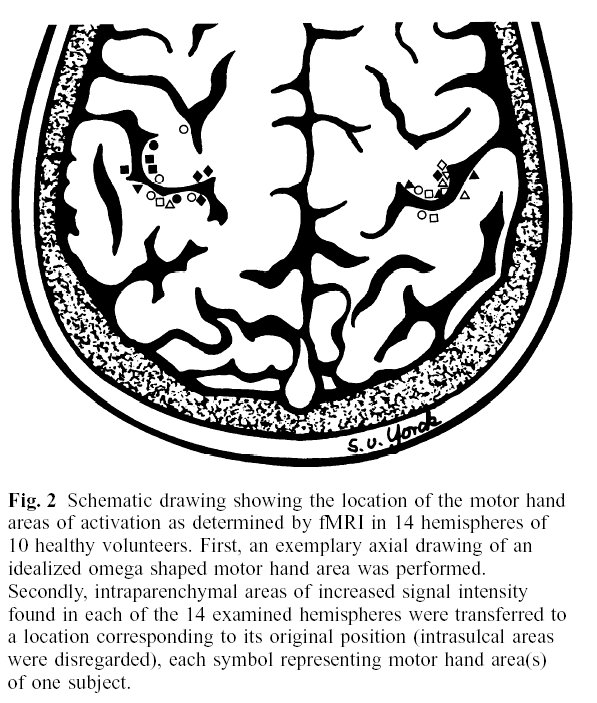
Motor & Action Areas
M1 (Primary Motor Cortex)
- The hand area of motor cortex is found on an upside-down omega part (in axial view) of the central sulcus
(Yousry et al., 1997, Brain)
FEF (Frontal Eye Fields)
(upper blobs)
(Muri et al., 1996, J Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry)
Premotor Cortex
- See Picard & Strick, 2001 for an excellent review - main points summarized below
(Picard & Strick, 2001, Curr Op Neurobiology)
Supplementary Motor Cortex
SMA or SMA-proper (Supplementary Motor Area)
- Posterior to VCA (coronal slice at anterior commissure)
- Likely homologue of monkey F3
- Direction connections to M1 and spinal cord
Pre-SMA (Pre-Supplementary Motor Area)
- Cognitive, sensory or motivation inputs for motor behavior
- Connected with prefrontal cortex
- Visuomotor associations (and auditory-motor too)
- Poor somatotopic organization
- Activation during working memory delays
Cingulate Motor Areas
Caudal Cingulate Zone (CCZ)
- Primarily related to movement execution
- Comparable to CMAd (caudal cingulate motor area, dorsal bank of cingulate sulcus)
- Primarily related to movement execution
- Area activated by pain is below CCZ
Rostral Cingulate Zone (RCZ)
- Motor and cognitive
- Attentional or arousal are more rostral and ventral
- Suggested roles in 'conflict monitoring' (anterior, RCZa) and 'attention/selection for action' (posterior, RCZp)
Dorsal (Lateral) Premotor Cortex (PMd)
(Tomassini et al., 2007, J Neurosci)
(Chouinard & Paus, 2006, The Neuroscientist)
pre-PMd = rostral (PMdr)
- Likely comparable to monkey F7
- Eye movement signals
- Activated by conditional motor tasks, visual cues, movement imagination
PMd proper = caudal (PMdc)
- Likely comparable to monkey F2
- Hand movement signals
- Movement preparation or execution
Ventral (Lateral) Premotor Cortex (PMv)
- In monkeys: densely interconnected with M1, contains F4 and F5 (F5 has canonical neurons that respond to visual objects and mirror neurons that respond to actions of another individual)
- In humans: ventral to FEF, but poorly characterized
- Some believe area 44 (Broca's area) in humans is comparable to F5 in monkeys but this is controversial